Understanding the Prostate: Functions, Anatomy, and Importance
Introduction,
The prostate is a vital component of the male reproductive system, yet it remains a source of mystery and concern for many men. This small, walnut-sized gland plays a crucial role in reproductive health and can impact overall well-being. In this post, we’ll explore the functions, anatomy, and significance of the prostate, aiming to demystify this important organ.
Anatomy of the Prostate
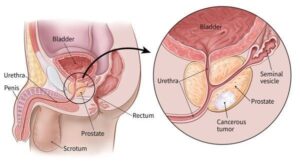
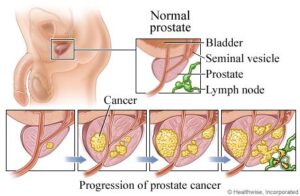
The prostate is located just below the bladder and in front of the rectum. It surrounds the urethra, the tube through which urine flows from the bladder out of the body. The gland is divided into several zones, with the peripheral zone being the most significant area where prostate cancer often develops.
Functions of the Prostate
Seminal Fluid Production: The primary function of the prostate is to produce a fluid that, together with sperm cells from the testicles and fluids from other glands, makes up semen. This prostatic fluid is slightly alkaline, which helps to neutralize the acidity of the vaginal tract, prolonging the lifespan of sperm.
Sperm Motility: The enzymes and proteins in the prostatic fluid support the motility and longevity of sperm, increasing the chances of successful fertilization.
Hormonal Conversion: The prostate also plays a role in hormone metabolism, particularly in converting testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a more potent androgen that influences prostate growth and function.
Importance of Prostate Health
Maintaining prostate health is crucial for several reasons:
Reproductive Health: A healthy prostate ensures proper seminal fluid production, which is essential for fertility.
Urinary Function: Since the prostate surrounds the urethra, any enlargement or inflammation can affect urinary function, leading to symptoms like difficulty in urination or increased frequency.
Disease Prevention: Conditions such as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), prostatitis, and prostate cancer are common, particularly as men age. Regular check-ups and awareness of prostate health can aid in early detection and treatment of these conditions.
Common Prostate Issues
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH): This non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate is common in older men and can cause urinary symptoms due to the compression of the urethra.
Prostatitis: Inflammation of the prostate, which can be acute or chronic, often caused by bacterial infection. Symptoms include pelvic pain, urinary issues, and sometimes flu-like symptoms.
Prostate Cancer: One of the most common cancers in men, prostate cancer can be slow-growing or aggressive. Early detection through screenings like PSA tests is vital for effective treatment.
Maintaining Prostate Health
Regular Screenings: Men over 50, or those with a family history of prostate issues, should have regular prostate exams and PSA tests.
Healthy Diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats can support prostate health. Foods like tomatoes (high in lycopene), broccoli, and green tea have been linked to a reduced risk of prostate problems.
Exercise: Regular physical activity helps maintain a healthy weight and hormone balance, both of which are beneficial for prostate health.
Hydration: Adequate fluid intake ensures proper urinary function and helps flush out potential toxins from the body.
Avoid Risk Factors: Reducing alcohol intake, quitting smoking, and managing stress can lower the risk of prostate issues.
Conclusion
Understanding the prostate’s functions, anatomy, and importance is the first step in maintaining optimal prostate health. Regular check-ups, a healthy lifestyle, and being aware of the signs and symptoms of potential prostate problems can significantly impact your overall health and well-being. By taking proactive steps, men can support their reproductive health and prevent complications associated with this vital gland.
